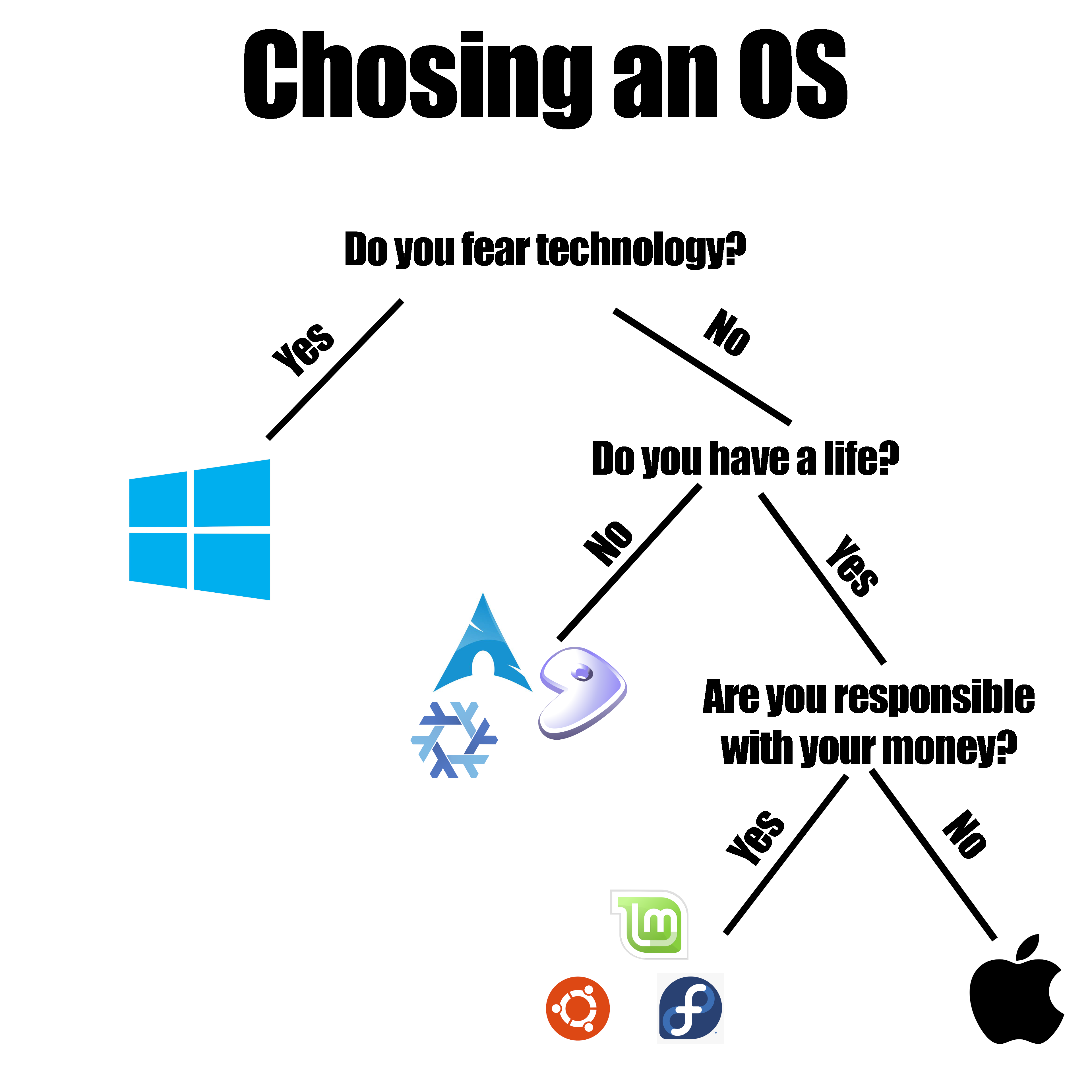
You're about to take your first steps in the wonderful world of Linux, but you're overwhelmed by the amount of choices? Welcome to this (I hope) very simple guide :)
The aim of this guide is to provide simple, clear information to ease your transition as a beginner. This is not a be-all-end-all guide nor an advanced guide. Because there is a lot of info and explanations everywhere, I will often (over-)simplify so as to keep the information accessible and digestible. Please refrain from asking to add your favorite distro/DE in the comments, I feel there is too much choice already ;)
Preamble
Make sure your hardware is compatible
Nowadays most relatively recent hardware works perfectly fine on Linux, but there are some edge cases still. If you don't use niche hardware and your wifi card is supported, chances are you're golden. Please note that nVidia is a bad faith player in the Linux world, so if you have a GeForce GPU, expect some trouble.
Make sure your favourite apps are either available or have a good replacement on Linux
If some proprietary app is essential to your workflow and is irreplaceable, consider running it in a VM, keeping a Windows partition for it or try and run it through Wine (this is advanced stuff though).
Be aware that Linux is not Windows/MacOS
Things work differently, and this is normal. You will probably struggle at the beginning while adjusting to a new paradigm. You may have to troubleshoot some things. You may break some things in the process. You will probably get frustrated at some point or another. It's okay. You're learning something new, and it can be hard to shed old habits forged by years on another system.
When in doubt, search for documentation
Arch Wiki is one of the greatest knowledge bases about Linux. Despite being heavily tied to Arch, most of its content is readily usable to troubleshoot most modern distros, as the building blocks (Kernel, systemd, core system apps, XOrg/Wayland, your DE of choice etc.) are the same. Most distros also maintain their own knowledge base.
Understanding the Linux world
What is Linux?
Linux, in the strictest definition, is the kernel, ie. the core component that, among other things, orchestrates and handles all interactions between hardware and software, of a large family of operating systems that, by metonymy, are called "Linux". In general understanding, Linux is any one of these operating systems, called distros.
What is a distro?
A distro, short for "Software Distribution", is a cohesive ensemble of software, providing a full operating system, maintained by a single team. Generally, all of them tend to provide almost the same software and work in a very similar way, but there are major philosophical differences that may influence your choice.
What are the main differences between distros?
As said above, there are a lot of philosophical differences between distros that lead to practical differences. There are a lot of very different ways the same software can be distributed.
- "Point Release" (OpenSUSE Leap) vs. "Rolling Release" (OpenSUSE Tumbleweed): Point release distros are like traditional software. They have numbered releases, and between each one no feature updates take place, only security updates and bug fixes. Rolling Release distros package and distribute software as soon as it's available upstream (the software developer's repos), meaning that there are no versions and no specific schedule.
- "Stable" (Debian Stable) vs. "Bleeding edge" (Arch): Stable distros are generally point release, and focus on fixing bugs and security flaws at the expense of new features. Each version goes through a lenghty period of feature freeze, testing and bug fixing before release. Stability here not only means trouble-free operation, but more importantly consistent behavior over time. Things won't evolve, but things won't break. At least until the next release. Bleeding edge distros, which often follow the rolling release model (there are outliers like Fedora which are mostly bleeding edge yet have point releases), on the other hand, are permanently evolving. By constantly pushing the latest version of each software package, new features, new bugs, bug fixes, security updates and sometimes breaking changes are released continuously. Note that this is not a binary, there is a very large continuum between the stablest and the most bleeding edge distro.
- "Community" (Fedora) vs. "Commercial" (RHEL): Despite the name, Community distros are not only maintained by volunteers, but can also be developed by some company's employees and can be sponsored by commercial entities. However, the main difference with Commercial distros is that they're not a product destined to be sold. Commercial distros like Red Hat's RHEL, SuSE Linux Enterprise or Ubuntu Pro are (supposed to be) fully maintained by their company's employees and target businesses with paid support, maintenance, fixes, deployment, training etc.
- "x package manager" vs. "y package manager", "x package format" vs. "y package format": It doesn't matter. Seriously.
apt, dnf or pacman, to name a few, all have the exact same purpose: install and update software on your system and manage dependencies.
- "general purpose" (Linux Mint) vs. "niche" (Kali Linux): General purpose distros are just that: distros that can do pretty much anything. Some are truly general purpose (like Debian), and have no bias towards any potential use, be it for a server, a desktop/laptop PC, some IOT or embedded devices, containers etc., some have various flavors depending on intended use (like Fedora Workstation for desktops and Fedora Server for, you guessed it, servers) but are still considered general purpose. They aim for maximum hardware compatibility and broad use cases. At the opposite end, niche distros are created for very specific and unique use cases, like pentesting (Kali), gaming (Nobara), music production (AV Linux) etc. They tend to have a lot of specific tools preinstalled, nonstandard defaults or modified kernels that may or may not work properly outside of their inteded use case.
- "team" (Any major distro) vs. "single maintainer" (Nobara): Pretty self explanatory. Some distros are maintained by a single person or a very small group of people. These distros do not usually last very long.
- "traditional" (Fedora Workstation) vs. "atomic" (Fedora Silverblue): In traditional distros, everything comes from a package. Every single component is individually installable, upgradeable, and deletable. Updating a package means deleting its previous version and replacing it with a new one. A power failure during an update lead to a partial upgrade and can make a system unbootable. Maybe a new package was bad and breaks something. Almost nothing prevents an unsuspecting user from destroying a core component. To mitigate risks and ensure a coherent system at each boot, atomic (also called transactional or immutable) distros, pioneered by Fedora Silverblue and Valve's SteamOS, were born. Like mobile phone OSes, the base system is a single image, that gets installed, alongside the current running version and without modifying it, and becomes active at the next reboot. As updates are isolated from one another, if the new version doesn't work the user can easily revert to a previous, functional version. Users are expected to install Flatpaks or use Distrobox, as installing (layering) packages is not as straightforward as with standard distros.
- "OG" (Debian) vs. "derivative" (Ubuntu): Original distros are directly downstream of their components' source code repositories, and do most of the heavy lifting. Because of the tremendous amount of work it represents, only a few distros like Debian, Arch, Slackware or Fedora have the history, massive community and sometimes corporate financial backing to do this. Other distros reuse most packages from those original distros and add, replace or modify some of them for differenciation. For example, Debian is the parent of almost all deb-based distros like Ubuntu, which itself is the parent of distros like Mint or Pop!_OS.
What are the main components of a distro, ie. a Linux-based operating system?
All distros provide, install and maintain, among other things, the following components:
- Boot and core system components (these are generally out-of-scope for beginners, unless you need to fix something, but you should at least know they exist):
- A boot manager (GRUB, systemd_init, etc.): Boots the computer after the motherboard POSTs, lets you choose what to start
- An init system (systemd, etc.): Starts everything needed to run the computer, including the kernel
- A kernel (Linux): Has control over everything, main interface for software to discuss with hardware
- Command-line environment, to interact with he computer in text mode:
- A shell (bash, zsh, fish etc.): The main interface for command-line stuff
- Command-line tools (GNU, etc.): Standard suite of command-line tools + default tools chosen by the distro maintainers
- User-installable command-line tools and shells
- Graphical stack for desktop/laptop computers:
- Display servers (X11, Wayland compositors): Handle drawing stuff on screens
- A Desktop environment (Plasma, Gnome, XFCE etc.): The main graphical interface you'll interact with everyday.
- User-facing applications (browsers, text processors, drawing software etc.): Some are generally installed by default and/or are part of a desktop environment's suite of software, most are user-installable.
- A package manager (apt, dnf, pacman, yast etc.): Installs, deletes, updates and manages dependencies of all software installed on the machine.
Which are the main Desktop Environments and which one should I choose?
As a new user, this is basically the only thing you should concern yourself about: choosing a first Desktop environment. After all, it will be your main interface for the weeks/years to come. It's almost as important as choosing your first distro. These are a few common choices that cater to different tastes:
- Gnome: Full featured yet very minimalist, Gnome is a great DE that eschews the traditional Desktop metaphor. Like MacOS, out of the box, it provides its strongly opinionated developers' vision of a user experience. Fortunately, unlike MacOS, there are thousands of extensions to tweak and extend the looks and behaviour of the DE. Dash-to-dock or Dash-to-panel are great if you want a more MacOS-like or Windows-like experience, Blur My Shell is great if you love blurry transparent things, Appindicator is a must, and everything else is up to you. Gnome's development cycle is highly regular and all core components and apps follow the same release schedule, which explains why a lot of distros choose it as their default DE.
- KDE Plasma: Full featured and maximalist, Plasma does not cater to a single design philosophy, is very flexible and can be tweaked almost ad infinitum. This may be an advantage for people who like to spend hours making the perfect environment, or a disadvantage as the possibilities can be overwhelming, and the added complexity may compromise stability, bugginess or completeness. There is not yet a single development cycle for core components and apps, which makes it a bit more difficult for distro maintainers and explains why there are so few distros with Plasma as the flagship DE. The KDE team is however evolving towards a more regular update cycle.
- Cinnamon: Forked from Gnome 3 by the Linux Mint team who disliked the extreme change of user experience it introduced, Cinammon provides a very traditional, "windows-like", desktop-metaphor experience in a more modern software stack than the older DEs it takes inspiration from. Cinnamon still keeps a lot in common with Gnome by being simple and easy to use, yet heavily modifiable with themes, applets and extensions.
- Lightweight DEs for old or underpowered machines: The likes of XFCE, LXDE, LXQt are great if you want to ressurect an old machine, but lack the bells and whistles of the aforementioned DEs. If your machine is super old, extremely underpowered and has less than a few Gb of RAM, don't expect miracles though. A single browser tab can easily dwarf the RAM usage and processing power of your entire system.
As for which one you should choose, this is entirely up to you, and depends on your preferences. FYI, you are not married to your distro's default desktop environment. It's just what comes preinstalled. You can install alternative DEs on any distro, no need to reinstall and/or distro-hop.
How do I install stuff on Linux?
Forget what you're used to do on Windows of MacOS: searching for your software in a seach engine, finding a big "Download" button on a random website and running an installer with administator privileges. Your package manager not only keeps you system up to date, but also lets you install any software that's available in your distro's repositories. You don't even need to know the command line, Gnome's Software or Plasma's Discover are nice graphical "App Stores" that let you find and install new software.
Flatpak are a great and more recent recent alternative to distro packages that's gaining a lot of traction, and is increasingly integrated by default to the aforementioned App Stores. It's basically a "universal" package manager system thet sits next to your system, that lets software developers directly distribute their own apps instead of offloading the packaging and distribution to distro maintainers.
Choosing a first distro
As discussed before, there is a metric fuckload (or 1.112 imperial fucktons) of distros out there. I advise you to keep it as mainstream as possible for your first steps. A distro with a large user base, backed by a decently large community of maintainers and contributors and aimed at being as fuss-free as possible is always better than a one-person effort tailored to a specific use-case. Choose a distro that implements well the DE of your choice.
What are great distros for beginners?
The following are great distros for beginners as well as more advanced users who just want to have a system that needs almost no configuration out of the box, just works and stays out of the way. Always read the installation documentation thoroughly before attempting anything, and follow any post-install requirements (for example, installing restricted-licence drivers on Fedora).
- Fedora Workstation: Clean, sensible, modern and very up to date and should work out of the box for most hardware. Despite being sponsored by Red Hat (who are getting a lot of justified hate for moving RHEL away from open-source), this is a great community distro for both beginners and very advanced users (including the Linus Torvalds). Fedora is the flagship distro for the Gnome Desktop Environment, but also has a fantastic Plasma version. Keywords: Point Release, close to Bleeding Edge, Community, dnf/rpm, large maintainer team, traditional, original.
- Linux Mint: Mint is an Ubuntu (or Debian for the LMDE variant) derivative for beginners and advanced users alike, that keeps Ubuntu's hardware support and ease of use while reverting its shenanigans and is Cinammon's flagship distro. Its main goal is to be a "just works" distro. Keywords: Point Release, halfway between Stable and Bleeding Edge, Community, apt/deb, smallish maintainer team but lots of contributors, traditional, derivative (Ubuntu or Debian).
- Pop!_OS: Backed by hardware Linux vendor System76, this is another Ubuntu derivative that removes Snaps in favor or Flatpaks. Its heavily modified Gnome DE looks and feels nice. In a few months/years, it will be the flagship distro for the -promising but still in development- Cosmic DE. Keywords: Point Release, halfway between Stable and Bleeding Edge, commercially-backed Community, apt/deb, employee's maintainer team, traditional, derivative (Ubuntu).
- If you want something (advertised as) zero-maintenance, why not go the Atomic way? They are still very new and there isn't a lot of support yet because they do things very differently than regular distros, but if they wort OOTB on your system, they should work reliably forever. Sensible choices are uBlue's Aurora (Plasma), Bluefin (Gnome) or Bazzite (gaming-ready), which are basically identical to Fedora's atomic variants but include (among other things) restricted-licence codecs and QOL improvements by default, or OpenSUSE's Aeon (Gnome). Keywords: Point Release, Bleeding Edge, Community, rpm-ostree, large maintainer team, Atomic, sub-project (Fedora/OpenSUSE).
Which power-user distros should I avoid as a beginner, unless I reaaaally need to understand everything instead of being productive day one?
These are amongst the very best but should not be installed as your first distro, unless you like extremely steep learning curves and being overwhelmed.
- Debian Stable: as one of the oldest, still maintained distros and the granddaddy of probably half of the distros out there, Debian is built like a tank. A very stringent policy of focusing on bug and security fixes over new features makes Debian extremely stable and predictable, but it can also feel quite outdated. Still a rock-solid experience, with a lot to tinker with despite very sensible defaults. It is an incredible learning tool and is as "Standard Linux" as can be. Debian almost made the cut to "beginner" distros because of its incredible reliability and massive amount of documentation available, but it might be a bit too involved for an absolute beginner to configure to perfection. Keywords: Point Release, Stable as fuck, Community, apt/deb, large maintainer team, traditional, original.
- Arch: The opposite of Debian in philosophy, packages often come to Arch almost as soon as the source code is released. Expect a lot of manual installation and configuration, daily updates, and regularly fixing stuff. An incredible learning tool too, that will make you intimate with the inner workings of Linux. The "Arch btw" meme of having to perform every single install step by hand has taken a hit since Arch has had a basic but functional installer for a few years now, which is honestly a good thing. I work in sofware. A software engineer who does every single tedious task manually instead of automating it is a shit software engineer. A software engineer who prides themself from doing every single tedious task manually should seriously reconsider their career choices. Arch's other main appeal is the Arch User Repository or AUR, a massive collection of user-created, automated install scripts for pretty much anything. Keywords: Rolling Release, Bleeding-edge, Community, pacman/pkg, large maintainer team, traditional, original.
Which distro should I avoid, period?
- Ubuntu: despite having a huge mind-share as the beginner distro, Ubuntu suffers from it's parent company's policy to make Ubuntu kinda-Linux-but-not-really and a second-rate citizen compared to their Ubuntu Pro commercial product. Some of the worst takes in recent years have been pushing Snaps super agressively in order to get some "vendor-lock-in", proprietary walled-garden ecosystem with exclusive commercial apps, forcibly installing snaps even when explicitely asking for a .deb package through
apt, baking ads and nags into major software or only delivering critical security patches to Pro customers. Fortunately, there are some great derivatives like Mint or Pop!_OS cited above that work equally well but revert some of the most controversial decisions made by Canonical.
- Manjaro: Manjaro might seem appealing as a "user-friendlier" Arch derivative and some of its tools are fantastic to remove some configuration burden, but ongoing mismanagement issues and the fact that it needs Arch-style regular maintenance as updates often break stuff prevent it from being a truly beginner distro. Manjaro also has a highly irregular update schedule that's weeks behind Arch, making using the AUR extremely dangerous, as it always expects a fully up-to-date Arch system.
- Any single-maintainer or tiny team distros like Nobara or CachyOS. They might be fantastic distros made by exceptional people (I have mad respect for Nobara's maintainer Glorious Eggroll and his work on Proton-GE), they are most often derivatives so the heavy lifting is already done by their parent distro's maitainers, but there is too much risk involved. Sometimes life happens, sometimes people move on to other projects, and dozens of small distros get abandonned every year, leaving their users dead in the water. Trusting larger teams is a much safer bet in the long term.
- Anything that refuse to use standards for ideological reasons like Alpine Linux, Devuan or Artix. Don't get me wrong, not using any GNU tools or systemd is a cool technological feat and developing alternatives to the current consensus is how things evolve. However, these standard tools have a long history, hundreds if not thousands of maintainers and are used by millions, meaning there's a huge chance your specific issue is already solved. Refusing to use them should be reserved to very advanced users who perfectly understand what they're gaining and losing. As a beginner to intermediate level, it will at best make most of the documentation out there irrelevant, at worst make your life a miserable hell if you need to troubleshoot anything.
Philosophical questions, or "I've seen people arguing over the Internet and now I'm scared"
You've done your research, you're almost ready to take the plunge, you even read a lot of stuff on this very community or on the other website that starts with a "R", but people seem very passionately for or against stuff. What should you do?
Shoud I learn the command line?
Yes, eventually. To be honest, nowadays a lot of things can be configured on the fly graphically, through your DE's settings. But sometimes, it's much more efficient to work on the command line, and sometimes it's the only way to fix something. It's not that difficult, and you can be reasonably productive by understanding just about a dozen very simple commands.
I have a very old laptop/desktop, should I use a distro from its era?
Noooo!. Contrary to Windows and MacOS which only work correctly on period-correct computers, Linux runs perfectly well on any hardware from the last 20 to 30 years. You will not gain performance by using an old distro, but you will gain hundreds of critical security flaws that have been since corrected. If you need to squeeze performance out of an old computer, use a lightweight graphical environment or repurpose it as a headless home server. If it's possible, one of the best ways to breathe new life into an old machine is to add some RAM, as even lightweight modern sofware will struggle with less than a few Gb.
Should I be concerned about systemd?
No. In short, systemd is fine and all major distros have switched to systemd years ago. Even the extremely cautious people behind Debian have used systemd as default since 2015. Not wanting to use systemd is a niche more rooted in philosophical and ideological rather than practical or technical reasons, and leads to much deeper issues than you should concern yourself with as a beginner.
Should I be concerned about XOrg/Wayland?
Yes and No, but mostly No. First off, most distros install both Wayland and XOrg by default, so if one is not satisfying to you, try the other. Remember in the preamble when I said nVidia was a bad actor? Well, most of people's complaints about Wayland are because of nVidia and their shitty drivers, so GTX/RTX users should stay on XOrg for now. But like it or not, XOrg is dead and unmaintained, and Wayland is the present and future. XOrg did too many things, carried too many features from the 80's and 90's and its codebase is a barely maintainable mess. X11 was born in a time when mainframes did most of the heavy lifting and windows were forwarded over a local network to dumb clients. X11 predates the Internet and has basically no security model. Wayland solves that by being a much simpler display protocol with a much smaller feature set adapted to modern computing and security. The only downside is that some very specific functionalities based on decades of X11 hacking and absolute lack of security can be lost.
I want to play some games, should I look for a gaming distro?
No. General purpose distros are perfectly fine for gaming. You can install Steam, Lutris, Heroic, Itch etc. and use Proton just fine on almost anything. Even Debian. In short, yes, you can game on Linux, there are great tutorials on the internet.
Should I be concerned about Flatpaks and/or Snaps vs. native packages?
Not really. Flatpaks are great, and more and more developers package their apps directly in Flatpak format. As a rule of thumb, for user facing applications, if your app store gives you the choice between Flatpak and your native package manager version, choose the most recent stable version and/or the one packaged by the developer themselves (which should often be the Flatpak anyway). Snaps however are kinda bad. They are a Canonical/Ubuntu thing, so as long as you avoid Ubuntu, its spins and its derivatives that still include Snaps, you should be fine. They tend to take a lot longer to startup than regular apps or Flatpaks, the snap store is proprietary, centralized and Canonical controls every part of it. Also, Canonical is very aggressive in pushing snaps to their users, even forcing them even when they want to install an apt package. If you don't care, have fun.
I need/want program "x", but it is only available on distro "y" and not on mine. I've been told to ditch my beloved distro and install the other one, should I?
No. Generally, most software is intallable from your distro's package manager and/or Flatpak. But sometimes, your distro doesn't package this program you need, or an inconsiderate developer only distributes a random .deb on their Github release page. Enter Distrobox. It is a very simple, easy to use command line tool that automates the creation of other Linux distros containers using Docker or Podman (basically, tiny, semi-independant Linuxes that live inside your regular Linux), and lets you "export" programs installed inside these containers to you main system so you can run them as easily and with almost the same performance as native programs. Some atomic distros like uBlue's variants even include it by default. That .deb we've talked about before? Spin a Debian container and dpkg install the shit out of it. Absolutely need the AUR? Spin an Arch container and go to town.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to everyone who helped improve this guide: @GravitySpoiled@lemmy.ml, @tkn@startrek.website, @throwaway2@lemmy.today, @cerement@slrpnk.net, @kzhe@lemm.ee, @freijon@feddit.ch, @aarroyoc@lemuria.es, @SexualPolytope@lemmy.sdf.org, @Plopp@lemmy.world, @bsergay@discuss.online ...and many others who chimed in in the comments <3
Link to version 1: https://lemm.ee/post/15895051